Spent the day doing a bunch of different filtering techniques in EIGRP and stumbled upon something new regarding metric filtering that I haven’t seen before so felt like it was worth a post. 🙂
EIGRP: Lab 04 Prefix List Filtering Published by Fajar Maulana Utbah Nurrochman on Sebelumnya, kita sudah melakukan Filtering Distribute List IN dan OUT,pada kesempatan kali ini kita akan belajar bagaimana cara filtering dengan prefix-list. The difference being that R1's prefix has an EIGRP RD of 500, and R3 has an EIGRP RD of 1000. The primary difference is that a prefix-list allows you to examine, and filter based on the prefix, and prefix-length, regardless of singular or a range of prefixes and prefix lengths. This allows greater flexibility in what we can filter.
Lab 1 – Filtering with prefix-lists
Eigrp Prefix List Meaning
- Configure a prefix-list on R4 that only blocks its loopback out on Gi1.45
- Configure a prefix-list on R1 so it doesn’t accept any updates from R4 on Gi1.146
Before we start our filtering our routing table should look something like this:
Let’s start by creating a prefix-list that blocks our loopback and permits everything else.
R5 should no longer see the 150.1.4.4/32 over the Gi1.45 link:
Lab 2 – Filtering with standard ACLs
- Configure a standard ACL on R9 to filter out all routes sourced from R7 that have an odd number in the third octet
We need an access-list that only matches odd numbers in the third octet, we control this by using our wildcard-mask. In other words the first bit must always be set to 0 for the network to be accepted (even numbers).
As we can see, the only odd-numbered network found in our routing table now is R9s own 150.1.9.9/32.
Lab 3 – Filtering with extended ACLs
- Shutdown R5s ethernetlink to R4
- Use only extended ACLs to achieve the following:
- Reroute traffic destined to R4 & R6 Loopbacks to go via R2
- Reroute traffic destined to R1 & R2 Loopbacks to go via R3
- Reroute traffic destined to R7 & R9 Loopbacks to go via R1
When we use extended ACLs with distribute-lists remember that the source-field represents the update-source and destination-field the network address. By only closing R5’s Gi1.45 link the routing table looks like this, most of the traffic is routed over the DMVPN-cloud:
There might be a much easier way to do this, but the way I solved it was by blocking all possible “alternative” routes learned in the DMVPN so only the targeted router was accepted as a valid update-source. So if we start with R4 & R6 that we’re supposed to be routed towards R2, lets first create access-list that deny R1, R3 & R5 as update-sources for 150.1.4.4/32.
! R5
access-list 100 deny ip host 155.1.0.1 host 150.1.4.4
access-list 100 deny ip host 155.1.0.3 host 150.1.4.4
access-list 100 deny ip host 155.1.0.4 host 150.1.4.4
access-list 100 permit ip any any
router eigrp 100
distribute-list 100 in Tunnel0
The only way to reach 150.1.4.4 over the DMVPN should now be 155.1.0.2.
Jre for mac. To adjust the rest of the networks we just have do modify our ACL with more entries.
Loopback prefixes for R4 & R6 should now be routed to R2, R1 & R2 to R3, R7 & R9 to R1.
Lab 4 – Filtering with Offset Lists
- Configure an offset-list on R7 so traffic to 150.1.3.3/32 is routed to R6
- If the link to R6 is down, traffic should be rerouted directly to R3
Before we do any changes, here is how R7 sees the 150.1.3.3 network currently.
As R7 has a direct link to R3 with a decently low feasible distance, there’s no alternative route that matches the feasibility condition (adv. distance lower than 130816). But by making the current route less attractive we should be able to make R7 prefer the route to R6 instead as long as it’s up. First we create a simple ACL that matches our network.
We then offset the metric of our current route to make it less desirable.

Our routing table in R7 looks like this after the changes:

As we’re still receiving the route from R3 we have a backup if our link to R6 goes down.
Lab 5 – Filtering with administrative distance
- Configure AD filtering on R3 so traffic towards 150.1.7.7 is sent to R1
Should be pretty easy, as you maybe know we can set AD on either route or by neighbor + route, in our case we need to do the latter.
Lab 6 – Filtering with Route maps
This lab had something new that I haven’t seen before. The requirements we’re as follows:
- Configure on R4:
- Loopback1 – 160.1.4.4/32, redistribute to EIGRP with tag 4
- Loopback2 – 170.1.4.4/32, redistribute to EIGRP
- Configure a route-filter on R2 that denies routes with tag 4
- Configure a route-filter on R3 that denies routes with a metric between 120000 – 140000
- Filters should not affect any other routes advertised
Let’s start with the R4, shouldn’t be anything tricky. We need two prefix-lists to match the different Loopbacks and a route-map to tag the desired route.
If we check the routes learned on R2 now 160.1.4.4/32 should be tagged.
Looks good! Now just have to do a route-map and filter our incoming routes on R2.
We should now only see the 170.1.4.4 in R2.
And the final step, filter out routes based on metric. Before configuring anything our routing table looks like this on R2:
Matching by metric was new to me but it was pretty easy to find the command as it had to be done with a route-map in my mind. We use the match statement with metric, which has the following options:
For us to match metrics between 120,000 – 140,000 we set the “average” and use deviation-option.
The 150.1.x.x we’re earlier routed via Gi1.13 & Gi1.37 but should now be filtered out and now take a worse route with metrics above 140k.
Sweet! Reading is going pretty well currently, I sort of finished “Routing on IOS, IOS XE, IOS XR”, jumping over the chapters I haven’t read anything about yet (multicast/bgp/route manipulation etc to backtrack later). Just started “Internet Routing Architectures” that seems to be focused solely on BGP, fun times! 🙂
This chapter provides information about the following redistribution topics:
- Defining seed and default metrics
- Redistributing connected networks
- Redistributing static routes
- Redistributing subnets into OSPF
- Assigning E1 or E2 routes in OSPF
- Redistributing OSPF internal and external routes
- Configuration example: route redistribution for IPv4
- Configuration example: route redistribution for IPv6
- Verifying route redistribution
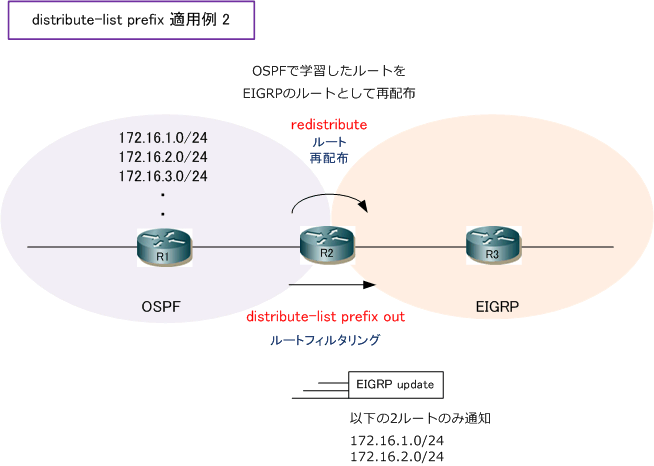
Route filtering using the distribute-list command
- Configuration example: inbound and outbound distribute list route filters
- Configuration example: controlling redistribution with outbound distribute lists
- Verifying route filters
Route filtering using prefix lists
- Configuration example: using a distribute list that references a prefix list to control redistribution
- Verifying prefix lists
Using route maps with route redistribution
- Configuration example: route maps
- Manipulating redistribution using route tagging
- Changing administrative distance for internal and external routes
- Passive interfaces
Defining Seed and Default Metrics
Eigrp Route Filtering Prefix List
Router(config)#router eigrp 100 | Starts the EIGRP routing process. |
Router(config-router)#network 172.16.0.0 | Specifies which network to advertise in EIGRP. |
Router(config-router)#redistribute rip | Redistributes routes learned from RIP into EIGRP. |
Router(config-router)#default-metric 1000 100 250 1 1500 Or | The metrics assigned to these learned routes will be calculated using the following components: |
Router(config-router)#redistribute rip metric 1000 100 250 1 1500 | 1000 = Bandwidth in Kbps |
100 = Delay in tens of microseconds | |
255 = Reliability out of 255 | |
1 = Load out of 255 | |
1500 = Maximum transmission unit (MTU) size | |
The metric keyword in the second option assigns a starting EIGRP metric that is calculated using the following components: 1000, 100, 255, 1 1500. |